By Johanna Budwig
The Curse Causeless Shall Not Come
FOREWORD
This author may very well go to jail for disclosing the facts contained in this booklet. You will read about a very serious subject: Cancer.
What you will read is the First Person account of how this author was cured of a malignant cancer of the descending colon by a simple dietary procedure. It is expected that this very book will be used against this author to establish legally the fact that he is practicing medicine without a license. He may be ordered by some Court to discontinue the future distribution of this book. Why? Cancer treatment, dear reader, is a major part of the multi-bill ion- dollar drug industry. You are being told, and it is now being subtly suggested to you by the many doctor type TV shows, that the American Cancer Society and the American Medical Association are leaving no stones unturned in an all out effort to “find the cause of cancer.” But at the very same time, every possible force and pressure is being applied to prevent doctors from using known and effective cancer cures. Instead, they are only permitted, by AMA agreement and government coercion through the Federal Food and Drug Administration, to treat cancer by means that they know are futile: Chemotherapy, cobalt radiation, and finally, the delaying tactic of surgery. Perhaps you think this is strong language! If the author dared, it would be even stronger: MURDER ONE.
The author’s grandfather died of colon cancer. The author’s father died of a cancer-related heart attack. His sister has cancer and has taken the Medical approach and is currently suffering from a series of unnecessary operations as her cancer strikes in first one place and then the other. None of these cancer victims were ever told by their Marcus Welby-type doctors that there are alternative choices; that there are valid and effective cancer cures that do not involve such radical surgery, expensive drugs and radiation. Any doctor who happens to stumble upon an effective treatment, or who develops one after years of research, may well be thrown into jail, harassed by the Courts in AMA initiated lawsuits, or driven out of the country.
It is widely known that cancer can be cured in Mexico, but unfortunately by the time the average cancer patient learns of such treatment, if indeed he ever does, the practitioners of the AMA have taken the last of his savings and insurance. With no money left, the patient is found to be “terminal” and sent home to die. For whatever good it may accomplish, and on behalf of the pitiful cancer patients now longing for the relief of death, this booklet is being published.
Nord W. Davis, Jr.
Magnesium – Mental Health Research Reviews
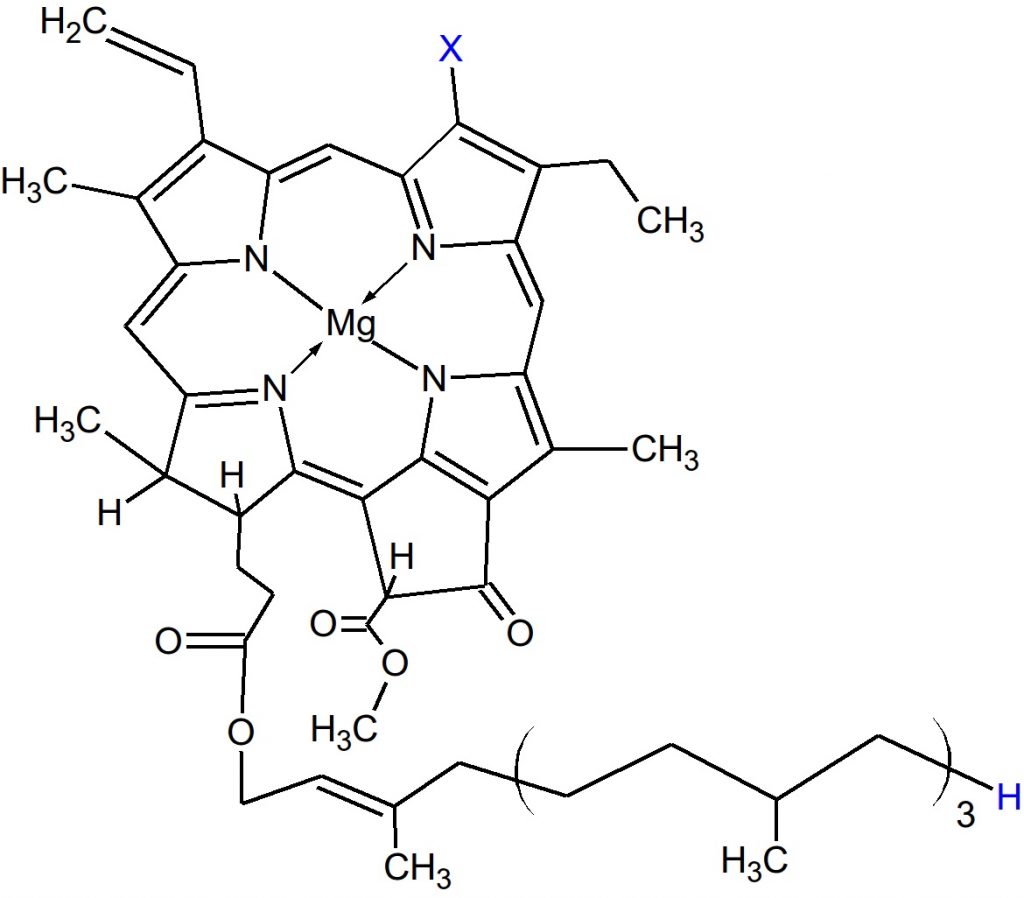
ChooseLife : Here will begin a cursory search into the scientific literature, regarding Magnesium. From the start I should note, that Reams said Chlorophyll was vital to the Liver, that for the Liver to supply the Pancreas with sufficient enzymes for it to regulate sugars properly, we need equivalent to 3oz of green juice daily (probably more nowadays), at the centre of Chlorophyll? Magnesium:
The Role of Magnesium in Neurological Disorders
Anna E. Kirkland,1Gabrielle L. Sarlo,1 and Kathleen F. Holton2,3,
Abstract
Magnesium is well known for its diverse actions within the human body. From a neurological standpoint, magnesium plays an essential role in nerve transmission and neuromuscular conduction.
It also functions in a protective role against excessive excitation that can lead to neuronal cell death (excitotoxicity), and has been implicated in multiple neurological disorders.
Due to these important functions within the nervous system, magnesium is a mineral of intense interest for the potential prevention and treatment of neurological disorders.
Current literature is reviewed for migraine, chronic pain, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke, as well as the commonly comorbid conditions of anxiety and depression.
Previous reviews and meta-analyses are used to set the scene for magnesium research across neurological conditions, while current research is reviewed in greater detail to update the literature and demonstrate the progress (or lack thereof) in the field. There is strong data to suggest a role for magnesium in migraine and depression, and emerging data to suggest a protective effect of magnesium for chronic pain, anxiety, and stroke. More research is needed on magnesium as an adjunct treatment in epilepsy, and to further clarify its role in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Overall, the mechanistic attributes of magnesium in neurological diseases connote the macromineral as a potential target for neurological disease prevention and treatment.
Keywords: magnesium, excitotoxicity, glutamate, migraine, chronic pain, epilepsy, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke
Full Paper : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6024559/
Rapid recovery from major depression using magnesium treatment.
Abstract
Major depression is a mood disorder characterized by a sense of inadequacy, despondency, decreased activity, pessimism, anhedonia and sadness where these symptoms severely disrupt and adversely affect the person’s life, sometimes to such an extent that suicide is attempted or results.
Antidepressant drugs are not always effective and some have been accused of causing an increased number of suicides particularly in young people.
Magnesium deficiency is well known to produce neuropathologies. Only 16% of the magnesium found in whole wheat remains in refined flour, and magnesium has been removed from most drinking water supplies, setting a stage for human magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium ions regulate calcium ion flow in neuronal calcium channels, helping to regulate neuronal nitric oxide production. In magnesium deficiency, neuronal requirements for magnesium may not be met, causing neuronal damage which could manifest as depression.
Magnesium treatment is hypothesized to be effective in treating major depression resulting from intraneuronal magnesium deficits. These magnesium ion neuronal deficits may be induced by stress hormones, excessive dietary calcium as well as dietary deficiencies of magnesium.
Case histories are presented showing rapid recovery (less than 7 days) from major depression using 125-300 mg of magnesium (as glycinate and taurinate) with each meal and at bedtime. Magnesium was found usually effective for treatment of depression in general use. Related and accompanying mental illnesses in these case histories including traumatic brain injury, headache, suicidal ideation, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, postpartum depression, cocaine, alcohol and tobacco abuse, hypersensitivity to calcium, short-term memory loss and IQ loss were also benefited. Dietary deficiencies of magnesium, coupled with excess calcium and stress may cause many cases of other related symptoms including agitation, anxiety, irritability, confusion, asthenia, sleeplessness, headache, delirium, hallucinations and hyperexcitability, with each of these having been previously documented. The possibility that magnesium deficiency is the cause of most major depression and related mental health problems including IQ loss and addiction is enormously important to public health and is recommended for immediate further study. Fortifying refined grain and drinking water with biologically available magnesium to pre-twentieth century levels is recommended.
The Effect of Magnesium Deficiency on Neurological Disorders: A Narrative Review Article.
Xue W1,2, You J2, Su Y2, Wang Q1,3.
Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Magnesium (Mg) is an essential element for the body. It is a cofactor for ATP, DNA, and RNA and more than 600 enzymes. As it is similar to Ca2+, this element can also act as a cell signaling molecule and play multiple important roles in the nervous, muscle, and immune systems. Recent studies have associated Mg-deficiency with many neurological disorders, such as cerebral vasospasm, Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, and migraine. As it plays such a crucial role in human body, therefore, we summarized the role of Mg in neurological disorders to illustrate the symptoms caused by Mg-deficiency and the possible underlying mechanisms.
METHODS:
We critically discuss the role of it that we review the recent literature of magnesium. We also review the available data which are concerning the role of magnesium in neurological disorders.
RESULTS:
Magnesium is related to neurological disorders on the basis of the study of animals and humans experiments. Furthermore, these nervous systems related diseases include cerebral vasospasm, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke and migraine.
CONCLUSION:
Magnesium has effects on neurological disorders, such as its utility in cerebral vasospasm, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, stroke and migraine. So here we make a brief review to conclude it.
KEYWORDS:
Alzheimer’s disease; Magnesium; Migraine; Neurological disorders; Parkinson’s disease; Stroke PMID: 31223564 PMCID: PMC6570791
Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy.
Gröber U1, Schmidt J2, Kisters K3,4.
Abstract
Magnesium is the fourth most abundant mineral in the body. It has been recognized as a cofactor for more than 300 enzymatic reactions, where it is crucial for adenosine triphosphate (ATP) metabolism.
Magnesium is required for DNA and RNA synthesis, reproduction, and protein synthesis. Moreover, magnesium is essential for the regulation of muscular contraction, blood pressure, insulin metabolism, cardiac excitability, vasomotor tone, nerve transmission and neuromuscular conduction.
Imbalances in magnesium status-primarily hypomagnesemia as it is seen more common than hypermagnesemia-might result in unwanted neuromuscular, cardiac or nervous disorders.
Based on magnesium’s many functions within the human body, it plays an important role in prevention and treatment of many diseases. Low levels of magnesium have been associated with a number of chronic diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, cardiovascular disease (e.g., stroke), migraine headaches, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
KEYWORDS:
ADHD; Alzheimer’s disease; asthma; cardiovascular disease; diabetes mellitus; hypomagnesemia; magnesium
The Role of Nutrients in Protecting Mitochondrial Function and Neurotransmitter Signaling: Implications for the Treatment of Depression, PTSD, and Suicidal Behaviors
Jing Du,1,3,*#Ming Zhu,1,*Hongkun Bao,1Bai Li,1Yilong Dong,1Chunjie Xiao,1Grace Y. Zhang,3Ioline Henter,4Matthew Rudorfer,2 and Benedetto Vitiello2
Abstract
Numerous studies have linked severe stress to the development of major depressive disorder (MDD), and suicidal behaviors.
Furthermore, recent preclinical studies from our laboratory and others have demonstrated that in rodents, chronic stress and the stress hormone cortisol has caused oxidative damage to mitochondrial function and membrane lipids in the brain.
Mitochondria play a key role in synaptic neurotransmitter signaling by providing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), mediating lipid and protein synthesis, buffering intracellular calcium, and regulating apoptotic and resilience pathways.
Membrane lipids are similarly essential to central nervous system (CNS) function, because cholesterol, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and sphingolipids form a lipid raft region, a special lipid region on the membrane that mediates neurotransmitter signaling through G-protein coupled receptors and ion channels.
Low serum cholesterol levels, low antioxidant capacity, and abnormal early morning cortisol levels are biomarkers consistently associated with both depression and suicidal behaviors.
In this review, we summarize the manner in which nutrients can protect against oxidative damage to mitochondria and lipids in the neuronal circuits associated with cognitive and affective behaviors.
These nutrients include ω3 fatty acids, antioxidants (vitamin C and zinc), members of the vitamin B family (Vitamin B12 and folic acid) and magnesium. Accumulating data have shown that these nutrients can enhance neurocognitive function, and may have therapeutic benefits for depression and suicidal behaviors. A growing body of studies suggests the intriguing possibility that regular consumption of these nutrients may help prevent the onset of mood disorders and suicidal behaviors in vulnerable individuals, or significantly augment the therapeutic effect of available antidepressants. These findings have important implications for the health of both military and civilian populations.
Keywords: vitamin, oxidative stress, synaptic plasticity, lipid, suicide, zinc
The Severity of Depressive Symptoms vs. Serum Mg and Zn Levels in Postmenopausal Women
M. Stanisławska, M. Szkup-Jabłońska, A. Jurczak, S. Wieder-Huszla, A. Samochowiec, A. Jasiewicz, I. Noceń, K. Augustyniuk, A. Brodowska, B. Karakiewicz, D. Chlubek, and E. Grochans
Abstract
The aim of this study was to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in postmenopausal women, depending on serum Mg and Zn levels.
The study involved 171 postmenopausal women from Poland, who were not using menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). The intensity of depressive symptoms was evaluated using a standard research technique, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI).
The plasma Mg and Zn concentrations were measured. Depressive symptoms of different severity levels were diagnosed in 36.8 % of the women. The mean serum Mg level was 1.53 ± 0.28 mg/dL, and Zn level was 72 ±14 μg/dL.
The women with higher serum Mg and Zn levels had less depressive symptoms, and this observation is a precious information which can be used when planning depressive disorder prevention programmes.
Keywords: Depressive disorder, Postmenopause, Magnesium, Zinc
Magnesium in addiction – a general view.
Abstract
Addiction is a dysregulation of brain reward systems that progressively increases, resulting in compulsive drug use and loss of control over drug-taking.
Addiction is a brain disease.
There is evidence that magnesium deficit is involved in addiction to various addictive substances (heroin, morphine, cocaine, nicotine, alcohol, caffeine, and others). Magnesium is involved in all the stages of addiction. Magnesium deficit enhances the vulnerability to psychoactive substance addiction. Stress and trauma reduce the brain magnesium level and at the same time favor addiction development.
In experimental studies, administration of magnesium while inducing morphine dependence in rats reduced the dependence intensity. Magnesium reduces the NMDA receptor activity and the glutamatergic activity. Because stress and trauma induce hypomagnesemia with increased vulnerability to addiction, magnesium intake by people who are under prolonged stress could be a way to reduce this vulnerability and the development of addiction to different psychoactive substances.
Anxiety and depression appear to be associated with increases in drug-related harm and addictive substance use. Magnesium anxiolytic effect could be important for the antiaddictive action. Addiction is characterized by relapses. Magnesium deficiency may be a contributing factor to these relapses.
KEYWORDS:
addiction; cocaine; heroin; magnesium deficit; nicotine; stress; trauma
Efficacy of intravenous magnesium sulfate in the treatment of acute migraine attacks.
Demirkaya S1, Vural O, Dora B, Topçuoğlu MA.
Abstract
OBJECTIVE:
To study the efficacy and tolerability of 1 g of intravenous magnesium sulfate as acute treatment of moderate or severe migraine attacks.
BACKGROUND:
Migraine is a common disorder in which not only the pain but also the accompanying symptoms such as nausea and vomiting reduce activity and productivity of sufferers. Many drugs used for the treatment of acute migraine attacks have many side effects, are not well tolerated, are ineffective in some patients, or cannot be used during pregnancy or in patients with ischemic heart disease. Magnesium deficiency has been proposed to play a role in the pathophysiology of migraine, and recently treatment of migraine with magnesium has gained considerable interest.
METHODS:
This was a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled trial including 30 patients with moderate or severe migraine attacks. Fifteen patients received 1 g intravenous magnesium sulfate given over 15 minutes. The next 15 patients received 10 mL of 0.9% saline intravenously. Those in the placebo group with persisting complaints of pain or nausea and vomiting after 30 minutes also received 1 g magnesium sulfate intravenously over 15 minutes. The patients were assessed immediately after treatment, and then 30 minutes and 2 hours later. Intensity of pain, accompanying symptoms, and side effects were noted.
RESULTS:
All patients in the treatment group responded to treatment with magnesium sulfate. The pain disappeared in 13 patients (86.6%); it was diminished in 2 patients (13.4%); and in all 15 patients (100%), accompanying symptoms disappeared. In the placebo group, a decrease in pain severity but persisting nausea, irritability, and photophobia were noted in 1 patient (6.6%). Accompanying symptoms disappeared in 3 patients (20%) 30 minutes after placebo administration. All patients initially receiving placebo were subsequently given magnesium sulfate. All of these patients responded to magnesium sulfate. In 14 patients (93.3%), the attack ended; in 1 patient (6.6%), pain intensity decreased; and in all 15 patients (100%), accompanying symptoms disappeared. Both the response rate (100% for magnesium sulfate and 7% for placebo) and the pain-free rate (87% for magnesium sulfate and 0% for placebo) showed that magnesium sulfate was superior to placebo. Twenty-six patients (86.6%) had mild side effects which did not necessitate discontinuing treatment during magnesium sulfate administration.
CONCLUSION:
Our results show that 1 g intravenous magnesium sulfate is an efficient, safe, and well-tolerated drug in the treatment of migraine attacks. It is possible that magnesium sulfate could be used in a broader spectrum of patients than other drugs commonly used for attack treatment. In view of these results, the effect of magnesium sulfate in acute migraine should be examined in large-scale studies.
The Association between Serum Magnesium Levels and Depression in an Adult Primary Care Population
Emily K. Tarleton,1,*Amanda G. Kennedy,2Gail L. Rose,3Abigail Crocker,4 and Benjamin Littenberg5
Abstract
Depression is common, places a large burden on the patient, their family and community, and is often difficult to treat.
Magnesium supplementation is associated with improved depressive symptoms, but because the mechanism is unknown, it is unclear whether serum magnesium levels act as a biological predictor of the treatment outcome.
Therefore, we sought to describe the relationship between serum magnesium and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ, a measure of depression) scores. A cross-sectional analysis of medical records from 3604 adults (mean age 62 years; 42% men) seen in primary care clinics between 2015 and 2018, with at least one completed PHQ were included.
The relationship between serum magnesium and depression using univariate analyses showed a significant effect when measured by the PHQ-2 (−0.19 points/mg/dL; 95% CI −0.31, −0.07; P = 0.001) and the PHQ-9 (−0.93 points/mg/dL; 95% CI −1.81, −0.06; P = 0.037).
This relationship was strengthened after adjusting for covariates (age, gender, race, time between serum magnesium and PHQ tests, and presence of diabetes and chronic kidney disease) (PHQ-2: −0.25 points/mg/dL; 95% CI −3.33, −0.09; P < 0.001 and PHQ-9: −1.09 95% CI −1.96 −0.21; P = 0.015).
For adults seen in primary care, lower serum magnesium levels are associated with depressive symptoms, supporting the use of supplemental magnesium as therapy. Serum magnesium may help identify the biological mechanism of depressive symptoms and identify patients likely to respond to magnesium supplementation.
Keywords: magnesium, depression, primary care
Correlation of magnesium intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a major global public health problem in the worldwide and is increasing in aging populations. Magnesium intake may be one of the most important factors for diabetes prevention and management. Low magnesium intake may exacerbate metabolic abnormalities. In this study, the relationships of magnesium intake with metabolic parameters, depression and physical activity in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes were investigated.
Methods
This cross-sectional study involved 210 type 2 diabetes patients aged 65 years and above. Participants were interviewed to obtain information on lifestyle and 24-hour dietary recall. Assessment of depression was based on DSM-IV criteria. Clinical variables measured included anthropometric measurements, blood pressure, and biochemical determinations of blood and urine samples. Linear regression was applied to determine the relationships of magnesium intake with nutritional variables and metabolic parameters.
Results
Among all patients, 88.6% had magnesium intake which was less than the dietary reference intake, and 37.1% had hypomagnesaemia. Metabolic syndromes and depression were associated with lower magnesium intake (p < 0.05). A positive relationship was found between magnesium intake and HDL-cholesterol (p = 0.005). Magnesium intake was inversely correlated with triglyceride, waist circumference, body fat percent and body mass index (p < 0.005). After controlling confounding factor, HDL-cholesterol was significantly higher with increasing quartile of magnesium intake (p for trend = 0005). Waist circumference, body fat percentage, and body mass index were significantly lower with increase quartile of magnesium intake (p for trend < 0.001). The odds of depression, central obesity, high body fat percentage, and high body mass index were significantly lower with increasing quartile of magnesium intake (p for trend < 0.05). In addition, magnesium intake was related to high physical activity level and demonstrated lower serum magnesium levels. Serum magnesium was not significantly associated with metabolic parameters.
Conclusions
The majority of elderly type 2 diabetes who have low magnesium intake may compound this deficiency with metabolic abnormalities and depression. Future studies should determine the effects of increased magnesium intake or magnesium supplementation on metabolic control and depression in elderly people with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Magnesium, Diabetes, Metabolic control, Depression, Physical activity, Elderly
Magnesium for treatment-resistant depression: a review and hypothesis. – PubMed
Abstract
Sixty percent of cases of clinical depression are considered to be treatment-resistant depression (TRD). Magnesium-deficiency causes N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) coupled calcium channels to be biased towards opening, causing neuronal injury and neurological dysfunction, which may appear to humans as major depression.
Oral administration of magnesium to animals led to anti-depressant-like effects that were comparable to those of strong anti-depressant drugs. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) magnesium has been found low in treatment-resistant suicidal depression and in patients that have attempted suicide. Brain magnesium has been found low in TRD using phosphorous nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, an accurate means for measuring brain magnesium. Blood and CSF magnesium do not appear well correlated with major depression.
Although the first report of magnesium treatment for agitated depression was published in 1921 showing success in 220 out of 250 cases, and there are modern case reports showing rapid terminating of TRD, only a few modern clinical trials were found.
A 2008 randomized clinical trial showed that magnesium was as effective as the tricyclic anti-depressant imipramine in treating depression in diabetics and without any of the side effects of imipramine. Intravenous and oral magnesium in specific protocols have been reported to rapidly terminate TRD safely and without side effects.
Magnesium has been largely removed from processed foods, potentially harming the brain.
Calcium, glutamate and aspartate are common food additives that may worsen affective disorders.
We hypothesize that – when taken together – there is more than sufficient evidence to implicate inadequate dietary magnesium as the main cause of TRD, and that physicians should prescribe magnesium for TRD.
Since inadequate brain magnesium appears to reduce serotonin levels, and since anti-depressants have been shown to have the action of raising brain magnesium, we further hypothesize that magnesium treatment will be found beneficial for nearly all depressives, not only TRD.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19944540
ChooseLife : Has there ever been a more important time to eat your greens? Make Green Smoothies? Take Epsom Salts baths? or, a few grains of Epsom Salts in drinking water through the day?
Reams and the Bibles Clean Meats
When reading about the diets of others, I kept coming across this concept of clean meats, but never took any time to learn (long term Vegetarian).
However, now my girls are being raised on a diet with Animal matter, I find it much better to understand what may help, or, potentially harm my daughters vitality and growth.
So, we have the concept of “Clean Meats” as stated in Leviticus:

Now, alone this may be of great benefit, some may still find they do not feel good at all on meat. However for those who feel the need for animal matter in their diet, enter Dr Reams :
Dr Reams:
For six weeks I did tests on him, without any limiting of his diet whatever. And he was slowly getting worse. I took that information then and began to weigh it out, day by day by day.
I found out then, every day that he ate the unclean foods such as catfish, shrimp, lobster, pork, ham, bacon, sausage, pork chops, spare ribs, or whatnot, his energy dropped. In the other days, it either held its own or kind of gained a little. It’s so much easier to bring it down than it is to bring it up.
So what I found out was that the unclean meats digest in a period of three hours and the clean meats in a period of 18 hours average. Now that is a difference! When meats digest too fast, they throw too much high-powered energy into your system at one time, and it burns you up. I have seen many people in their late thirties or early forties. To look at them, you’d think they were in their late seventies because they had eat so much high-powered foods, until it burned them up.
Dr Reams and Dan Skow Food Class
ChooseLife : That, is huge data, huge, if anybody needs to understand it.
Carey Reams – Dan Scow : Cooking Class
This PDF came from : https://tandjenterprises.com/
There is an epic set of Data available there, if you seek to find it.
Gout Pushes Up Risk Of Kidney Disease
Aug. 28 (UPI) — People with gout have nearly a 30 percent higher risk of developing chronic kidney disease than people without gout, a new study says.
In addition, those with gout who receive dialysis or need a kidney transplant have more than a 200 percent higher chance of kidney failure than those without gout, according to research published Wednesday in BMJ Open.
Gout is inflammatory arthritis that causes uric acid to build up in the joints, often leading to extreme pain and even debilitation for some.
“While we always believed that high levels of uric acid might be bad for kidneys and that patients with gout may have a higher risk of kidney failure, we were quite surprised by the magnitude of the risk imposed by gout in these patients,” study author Austin Stack, a researcher at University of Limerick in Ireland, said in a news release. “We were particularly interested in the risk of advanced kidney disease, as these patients in general have a higher risk of kidney failure and death.”
The researchers looked at data for nearly 69,000 gout patients from another UK-based study to assess their risk of advanced chronic kidney disease. They compared that data to 554,964 patients without gout.
Diabetes, eating a lot of seafood and meat, drinking alcohol and obesity are all risk factors for gout, according to the Mayo Clinic.
According to the National Institutes of Health, nearly 4 percent of U.S. adults have gout. Over 661,000 people in the United States have kidney failure, including 468,000 on dialysis.
“The result of this new research suggests that gout may also play an important role in the progression of kidney disease,” Stack said. “The identification of gout as a potential risk factor opens up new opportunities for the prevention of kidney disease and its consequences.
pH : The Toxicity Arrow Piercing Modern Society

By ChooseLife
Why is it, that many modern diseases of high prevalence, affect some people and not others?
Well? It can’t be the Mercury, they said, as otherwise everyone would get it.
Well? It can’t be the Fluoride, our body needs and produces that.
Well? It can’t be the Aluminium, it’s prevalence means we have historical digestive capability to cope they say, it is such tiny amounts given medically they say.
Well? It can’t be poor diet, the body has homeostasis to set right such problems.
Until we start to look at life from another perspective, illness may hurtle towards us, regularly, with ever more velocity. Given the continual decline in soil quality, producing less vital fruits, vegetables, meats, nuts and seeds (even herbs). The problem is exacerbated by the emergence of processed sugars and flours, which in most guises are antagonistic to our biochemistry, chiefly Calcium (Magnesium, Iodine et al.), which might make a simple walk in the park dangerous, simply a cut or graze might cause an infection.
Why is it so? pH
When fluids in the endosome become too acidic, the cargo is trapped within the endosome deep inside the cell. When the endosome contents are more alkaline, the cargo lingers at the cell’s surface for too long.
They found that mouse cell lines containing the Alzheimer’s disease gene variant had more acidic endosomes (average of 5.37 pH) than cell lines without the gene variant (average of 6.21 pH).

The above research, clearly demonstrate that it is when pH of matter falls (or rises) out of its environmental bounds, matter starts to decay and becomes unable to buffer stronger opposing electromagnetic forces, demonstrated by the papers above showing it is pH dropping which really appears to make Mercury, Aluminium & Fluoride (Excessively) Toxic, even in the ‘low’ amounts suggested as safe by regulatory authorities.
This ticks all the boxes of “why some and not others” with Dental Amalgam, Vaccination related side effects (Aluminium Hydroxide pH 9.5 injected into an individual with a tissue pH in the 5.0-5.5 range is hugely more dangerous than an individual in the safer zone of 6-7 – the author believes this is the propellant of many debilitating diseases, the data presented in this article supports this theory).
So, we have a period eating poorly, high sugars, processed carbs, processed meats/dairy. Any part of this combination, as a core part of diet, to the wrong individual, will make the tissue pH plummet, it is all there in the studies. If individuals live like this, then the smallest of environmental pollutants may become lethal (because we lack the buffer system, which may allow the host sufficient robustness to cope, this is what gives the lymphatic system the traction to cycle these toxins out).
If you raise the pH of your terrain (eat more greens & more Omega 3!), you suddenly become less prone to infection and heavy metals become less toxic to you, it is almost like God was trying to pass a message to humanity through Carey Reams, isn’t it?
Higher Fruit and Vegetables, less meat, 22,000 people studied, raises pH of Urine:
In conclusion, a more alkaline diet, higher fruit and vegetable and lower meat intake were related to more alkaline urine with a magnitude similar to intervention studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18042305/
Effect of urine pH changed by dietary intervention on uric acid clearance mechanism of pH-dependent excretion of urinary uric acid
High meat after 3 days, urine pH drops to 5.9
High Fruit Veg after 3 days, urine pH rises to 6.7
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3406944/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2976726/
Study shows mean pH of Urine drops from 6.7 to 5.5 in people suffering diarrhea
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7702787
CONCLUSIONS:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29144608
Low urine pH is significantly associated with abnormal glucose tolerance; therefore, measuring urine pH might prove useful for identifying patients at high risk for diabetes.
Metabolic abnormalities in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
The majority of sufferers have urine pH below 5.5
https://academic.oup.com/ndt/article/30/2/197/2337167
Simply testing someones pH, may show clearly whether they have the biological capability, at all, to repel these neurotoxins, could life be so simple? (not that I advocate vaccination at all personally, or any unnecessary exposure to these nasty elements, full stop). However, If I was a worried parent, before deciding on vaccination I would test my childs urine pH, to get an indicator the gravity of danger my child faces. Then if their pH was below 6.0 maybe feed them more greens and good oil for a few weeks, test again, then make a more informed decision. This seems eminently sensible.
ChooseLife : pH balancing is the middle path. Developed from thoughts of Randall David Dew, it is time this great man was set free.
To note, the pH of the ‘high fruit and vegetable diet’, is higher than Carey Reams suggested we should attain, to produce perfect friction (or metabolic energy release between anionic and cationic elements in the body), he suggests 6.4 is perfect urine pH, the same for Saliva pH, which together denote the overall pH terrain status (the mean of 2x Urine 1x Saliva).
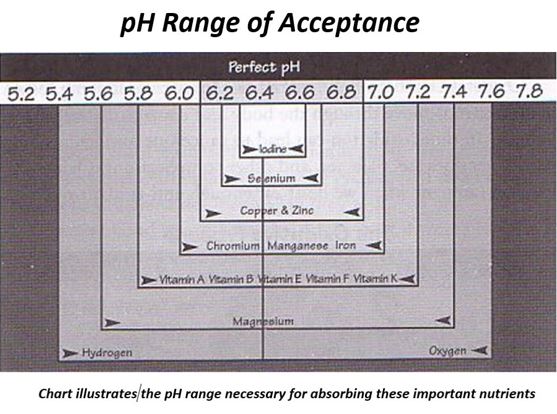
This is just a reflection, this is not advice.
Aluminium Toxicity pH Variable
Long-term toxicity to aquatic invertebrates
Toxicity decreased with increasing pH
Aluminium toxicity was reduced at high pH, but a larger reduction was observed when changing pH from 6 to 7 than from 7 to 8.
https://echa.europa.eu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/15529/6/2/5
Literature Review: Six long-term chronic toxicity studies to two species of aquatic invertebrates(Ceriodaphnia dubia and Daphnia magna) were identified as acceptable studies.
See Table # “Overview of long-term effect on aquatic invertebrates” (below). ECr10s were calculated using raw data provided from each study using the statistical program Toxicity Relationship Analysis Program (TRAP) version 1.10 from the US EPA National Health an Environmental Effects Research Laboratory (NHEERL).
All other endpoints were as reported in each study. NOECs and EC10s ranged from 0.076 to 4.9 mg Al/L and 0.021 to 0.997 mg Al/L, respectively. Water quality data for these studies suggest a direct relationship between toxicity and pH, hardness, and DOC. For studies that experimentally manipulated water quality (e.g., CIMM 2009 and 2010a ), toxicity decreased with increasing pH, hardness, and DOC.
Aluminum and water: reaction mechanisms, environmental impact and health effects
Aluminum naturally occurs in waters in very low concentrations. Higher concentrations derived from mining waste may negatively affect aquatic biocoenosis. Aluminum is toxic to fish in acidic, unbuffered waters starting at a concentration of 0.1 mg/L. Simultaneous electrolyte shortages influence gull permeability, and damage surface gull cells. Aluminum is mainly toxic to fish at pH values 5.0-5.5. Aluminum ions accumulate on the gulls and clog these with a slimy layer, which limits breathing. When pH values decrease, aluminum ions influence gull permeability regulation by calcium. This increases sodium losses. Calcium and aluminum are antagonistic, but adding calcium cannot limit electrolyte loss. This mainly concerns young animals. An aluminum concentration of 1.5 mg/L turned out to be fatal to trout. The element also influences growth of freshwater bony fish.
Full : https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/water/aluminium/aluminum-and-water.htm#ixzz5xTLuYJaV
Choose Life : Considering what is happening in the world in these times, these studies about aquatics, helps link so much together. This post will be updated as I find more data on this, just started a new job so bare with me please.
Carey Reams – Kathryn Kuhlman – The Holy Spirit Healings
It is a real shame that the Author didn’t include Carey Reams case with Kuhlman in his book. In ‘Choose Life Or Death’ Reams recounts that he was at the brink of death, after suffering shrapnel piercing, and lodging in, his Pancreas during military service.
This genius biochemist was not able to heal himself, he reflected that he felt he was in his last week of life, this is what precipitated his attendance of Kathryn Kuhlmans Healing Service. Reams tells how he had no faith in a healing, but was given glowing reference by someone, and everything else had failed him.
As we see at the very start of the video at the top, Reams was healed by the Holy Spirit!
After this point in Reams life he appears to change quite significantly, he talks of focusing on healing a boy ceaselessly, for days, like a deep meditative reflection (it is my belief that in such situations, the person may be able to connect/touch the universal consciousness, people who encounter near death, such as Reams, appear to perhaps create a soul version of ‘muscle memory’, where subsequently they gain a significant enhancement in ability to connect again to this source).
He comes to a profound realisation, after this sequence of events, that he understands a set of biological variables, which when he tests with some reasonably simple tools, can deduce the biological energy status of the host. This is what he terms Reams Biological Theory of Ionisation (RBTI). This developed understanding and testing methodology, coupled with his background as an agronomist, saw him become famous locally.
Two local Hospitals began to refer lost causes to him, during the next years:
Reams said: We tested over 24,000 people in 1970-1971. Over 10,000 of those came to us as “terminal”. We lost five. Those five we couldn’t keep alive for 30 days. (10K were referred to him directly by doctors for hopeless cases. He worked directly with a Florida hospital and doctors, often with the “hopeless cases.”)
Choose Life : I believe in miracles.
The Acid Test of Fluoride: How pH Modulates Toxicity
Abstract
Background
It is not known why the ameloblasts responsible for dental enamel formation are uniquely sensitive to fluoride (F−). Herein, we present a novel theory with supporting data to show that the low pH environment of maturating stage ameloblasts enhances their sensitivity to a given dose of F−. Enamel formation is initiated in a neutral pH environment (secretory stage); however, the pH can fall to below 6.0 as most of the mineral precipitates (maturation stage). Low pH can facilitate entry of F− into cells. Here, we asked if F− was more toxic at low pH, as measured by increased cell stress and decreased cell function.
Methodology/Principal Findings
Treatment of ameloblast-derived LS8 cells with F− at low pH reduced the threshold dose of F−required to phosphorylate stress-related proteins, PERK, eIF2α, JNK and c-jun. To assess protein secretion, LS8 cells were stably transduced with a secreted reporter, Gaussia luciferase, and secretion was quantified as a function of F− dose and pH. Luciferase secretion significantly decreased within 2 hr of F− treatment at low pH versus neutral pH, indicating increased functional toxicity. Rats given 100 ppm F− in their drinking water exhibited increased stress-mediated phosphorylation of eIF2α in maturation stage ameloblasts (pH<6.0) as compared to secretory stage ameloblasts (pH∼7.2). Intriguingly, F−-treated rats demonstrated a striking decrease in transcripts expressed during the maturation stage of enamel development (Klk4 and Amtn). In contrast, the expression of secretory stage genes, AmelX, Ambn, Enamand Mmp20, was unaffected.
Conclusions
The low pH environment of maturation stage ameloblasts facilitates the uptake of F−, causing increased cell stress that compromises ameloblast function, resulting in dental fluorosis.
Full : https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0010895
